==和equals的区别
equals方法
- equals:是Object类中的方法,只能判断引用类型,不能用于判断基本数据类型的变量
- 默认是判断地址是否相等,子类通常重写该方法,用来判断内容是否相等
- string
- Integer
String的equals源码分析
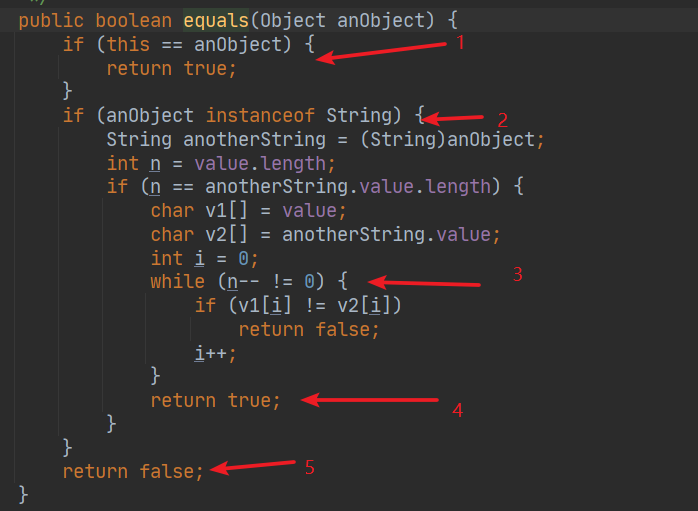
- 如果是同一个对象,就返回true
- 然后判断类型,通过强转类型向下转型
- 再判断长度是否一样,再一个一个地比较字符
- 如果两个字符串的所有字符都相等,返回true
- 如果比较不是字符串,则直接返回false
Integer的源码分析
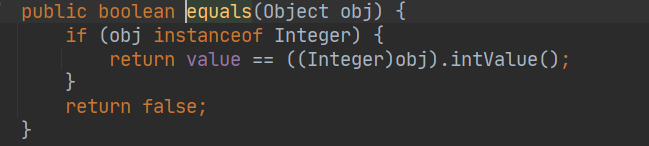
- 判断类型
- 再判断值
实例演示
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num1 = new Integer(1000);
Integer num2 = new Integer(1000);
System.out.println(num1.equals(num2));//引用类型,判断两个对象内容,为true
System.out.println(num1 == num2);//引用类型,判断两个对象地址是否相同,为false
//String类比与Integer
String str1 = new String("hello1");
String str2 = new String("hello1");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
int num3 = new Integer(1);
int num4 = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(num3 == num4);
//int是基本数据类型equals不能用于基本数据类型,所以没有equals方法
}
}
注意
- Object的equals方法默认就是比较对象地址是否相同,也就是判断两个对象是不是一个对象
- 不能用于基本数据类型的变量
- 子类通常重写该方法,用来判断内容是否相等
==运算符
- 如果比较的对象是基本数据类型,则比较的是数值是否相等
- 如果比较的是引用数据类型,则比较的地址值是否被相等
实例演示
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num1 = new Integer(1000);
Integer num2 = new Integer(1000);
System.out.println(num1.equals(num2));//引用类型,判断两个对象内容,为true
System.out.println(num1 == num2);//引用类型,判断两个对象地址是否相同,为false
//String类比与Integer
String str1 = new String("hello1");
String str2 = new String("hello1");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
int num3 = new Integer(1);
int num4 = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(num3 == num4);//true
//int是基本数据类型equals不能用于基本数据类型,所以没有equals方法
}
}
结论
- equals方法用来比较两个对象的内容是否相等,不能用于基本数据类型的变量;如果没有对equals方法重写,通常比较的是引用类型的变量所指向对象的地址;如果对equals方法重写,比较的是所指对象的内容,比如String、Integer还有Date等类型对equals方法进行了重写
- 如果比较的对象是基本数据类型,则比较的是数值是否相等;如果比较的是引用数据类型,则比较的地址值是否被相等

