SpringSecurity
web应用框架需要进行认证和授权,认证是验证当前访问系统的是不是本系统的用户,并且确定是哪个用户,授权:经过认证后判断当前用户是否有权限进行某个操作
引入SpringSecurity
项目pom.xml文件中直接引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
引入依赖后尝试访问之前的接口就会自动跳转到一个SpringSecurity的默认登录页面,默认用户名是user,密码会输出在控制台
认证
登录校验过程
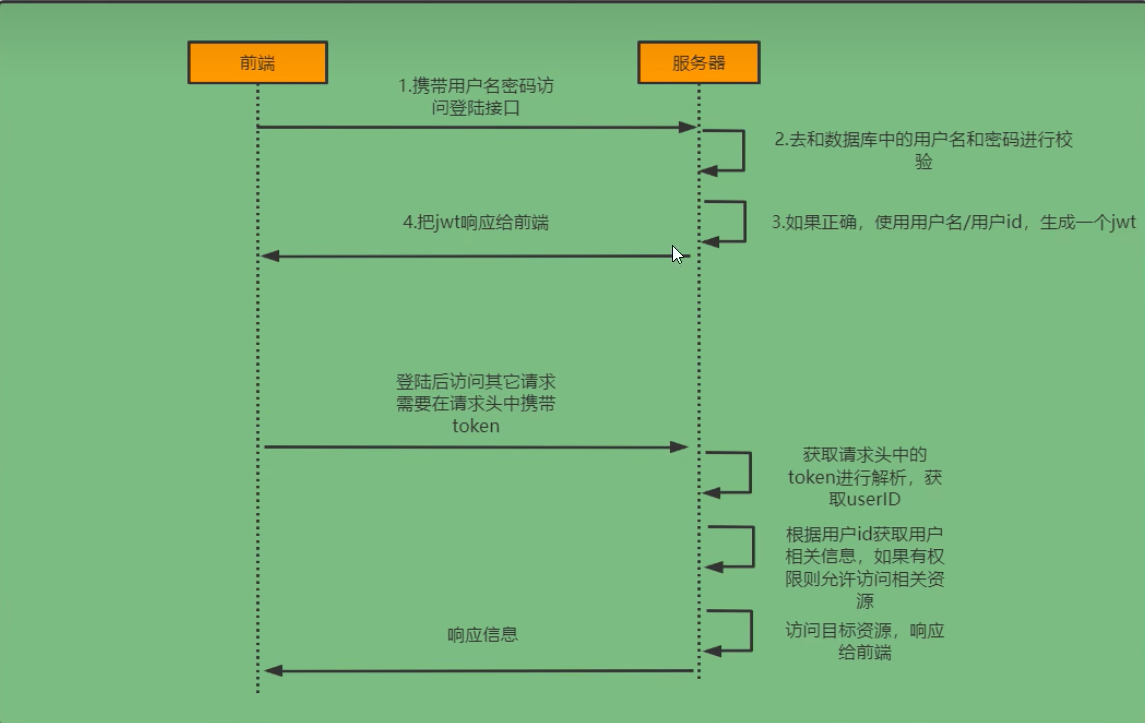
jwt全称Json-web-token,通过json的方式作为web应用中的令牌,用于在各方之间安全地将信息作为json对象传输
完整流程
springsecurity的原理其实就是一个过滤器链,内部包含了提供各种功能的过滤器。一些重要的过滤器
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter:负责处理在登录页面填写完用户名和密码的登录请求
ExceptionTranslationFilter:处理过滤器链中抛出的任何AccessDeniedException(用户在访问受保护资源时被拒绝而抛出的异常)和AuthenticationException(身份验证失败时抛出的安全认证异常)
FilterSecurityInterceptor:负责权限校验的过滤器
认证流程
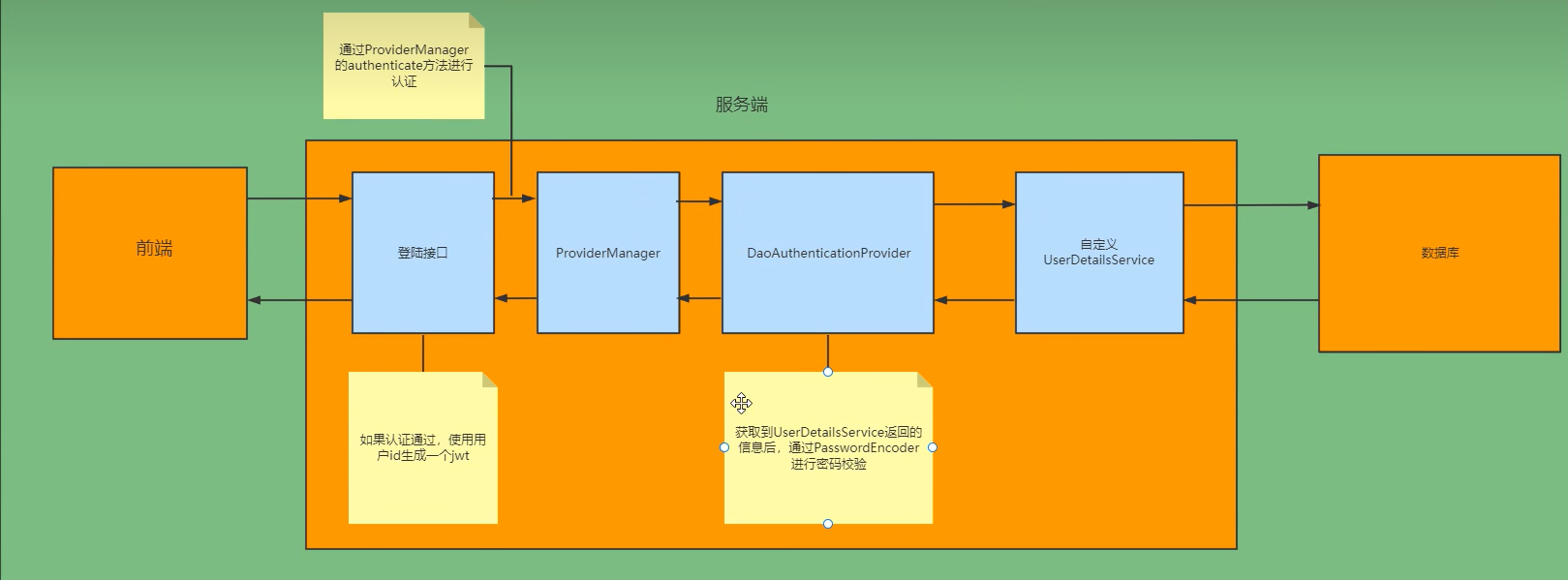
通过自定义UserDetailsService接口去查询数据库中对应的用户和权限信息,然后将去权限信息封装成UserDetails对象;自定义登录接口,调用ProviderManager的方法进行认证,认证通过生成jwt,将用户信息存入redis
前端携带token发起请求,怎样进行校验?
需要自己定义一个过滤器,jwt认证过滤器
1、获取token
2、解析token
3、获取userid
4、封装Authentication对象存入SecurityContextHolder,从中获取当前请求的用户信息
这样就会出现频繁地查询用户信息,所以在登录接口认证通过,使用用户id生成一个jwt,然后用userid作为key,用户信息作为value存入redis,就减少了了数据库频繁查询的压力
实现过程
数据库校验用户
1、添加依赖
<!--redis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--fastjson依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.33</version>
</dependency>
<!--jwt依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.0</version>
</dependency>
2、redis使用FastJson序列化
3、redis的一些配置
4、统一响应类
5、生成jwt的工具类
6、redis的工具类
7、字符串渲染到客户端的工具类
8、用户表的实体类
9、在数据库中创建用户表
10、添加mybatisplus和mysql的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置数据库信息
spring:
datasource:
url:jdbc:mysql://1ocalhost:3306/sg_security?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=uTc
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysq1.cj .jdbc.Driver
定义mapper接口
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User>{
}
修改user实体类
在类名上加上@TabName(value="sys_user"),id字段加上@TableId
配置mapper扫描
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScann("com.bai.mapper")
public class SimpleSecurityApplication{
public static void main(String[] args){
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(SimpleSecurityApplication.class);
}
}
实现UserDetailsService接口查询用户和对应的权限信息
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException{
//查询用户信息
LambdaQueryWapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(User::getUserName,username);
User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWapper);
//如果没有查到用户抛出异常
if(Objects.isNUll(user)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名或者密码错误");
}
return new LoginUser(user);
}
}
返回的如果是UserDetails,他是一个接口,需要实现他的方法,对他的方法进行重写
@Data
@NoArgsContructor
@AllArgsContructor
public class LoginUser implements UserDetails{
private User user;
}
密码加密存储
测试的时候为什么需要在数据库密码前面加{noop}
默认使用的PasswordEncoder要求数据库中的密码格式为 :{id}password,它会根据id去判断密码的加密格式。一般不会采用这种方式,需要替换PasswordEncoder
一般使用SpringSecurity提供的BCryptPasswordEncoder
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder{
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
登录接口
引入jwt的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidu</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
需要自定义登录接口然后让SpringSecurity对这个接口放行,让用户访问这个接口的时候不用登录也能发访问。
在接口中通过AuthenticationManager的authenticate方法来进行用户认证 ,需要在springSecurity配置中将AuthenticationManager注入容器。
认证成功后生成一个jwt返回,并且为了让用户下回请求时能通过jwt识别出具体的用户,需要吧用户存入redis,把用户的id作为key
controller
@RestController
public class LoginController{
@Autowired
private LoginService loginSerice;
@PostMapping("/user/login")
public ResponseResult login(@RequestBody User user){
// 登录
return loginService.login(user);
}
}
impl
@Service
public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginService{
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
public ResponseResult login(User user){
// AuthenticationManager authenticate进行用户认证
// 1.在SecurityConfig配置类重写authenticationManagerBean()
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getUserName(),user.gePassword());
Authentication authenticate = authenticationManager.authenticate(authenticationToken);
// 如果认证没通过,给出对应的提示
if(Objects.isNull(authenticate)){
throw new RuntimeException("登录失败");
}
// 如果认证通过,使用userId生成jwt
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser)authenticate.getPrincipal();
String userId = loginUser.getUser().getId().toString();
String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(userId);
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("token",jwt);
// 把完整的用户信息存入redis,userId为key
redisCache.setCaheObject("login:"+userId,loginUser);
return new ResponseResult(200,"登录成功",map);
}
}
service
public interface LoginService{
ResponseResult login(User user);
}
SecurityConfig
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter jwtAuthenticationTokenFilter;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder{
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authticationManagerBean() throws Exception{
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws exception{
http
//关闭csrf
.csrf().disable
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPoliy(SessionCreationPolict.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
//对于登录接口允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/user/login")
//除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authticated();
//添加过滤器
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationTokenFilter,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
认证过滤器
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequest{
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
protected void doFillterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain filterChain) throws {
//获取token
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if(!StringUtils.hasText(token)){
// 放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//解析token
try{
Claims claims = Jwt.parseJWT(token);
userId = claims.getSubject();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("token非法");
}
//从redis中获取用户信息
String redisKey = "login"+userId;
LoginUser loginUser = redisCache.getCacheObject(redisKey);
if(Objects.isNUll(loginUser)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户未登录");
}
//存入SecurityContextHolder
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser,null,null);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication();
// 放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
为什么不使用Filter实现接口
Filter会被多次调用执行过滤操作,换成spring提供的实现类,每个请求只会执行一次
退出登录
自定义接口获取SecurityContextHolder中的认证信息,删除redis中对应的数据即可
@RestController
public class LoginController{
@Autowired
private LoginService loginSerice;
@PostMapping("/user/login")
public ResponseResult login(@RequestBody User user){
// 登录
return loginService.login(user);
}
@RequestMapping("/user/logout")
public ResponseResult logout(){
return logService.logout();
}
}
impl
@Override
public ResponseResult logout(){
//获取SecurityContextHolder中的用户id
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication = (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser)authentication.getPrincipal();
Long userId = loginUser.getUser().getId();
//删除redis中的值
redisCache.deleteObject("login:"+userId);
return new ResponseResult(200,"注销成功");
}
授权
授权基本流程
在SpringSecurity中,会使用默认的FilterSecurityInterceptor来进行权限校验。在FilterSecurityInceptor中会从SecurityContextHolder获取其中的authentication,然后获取其中的权限信息,校验当前用户是否拥有访问的当前资源所需的权限,所以在项目中需要把当前用户的权限信息存入Authentication
授权实现
1、限制访问资源所需的权限
SpringSecurity提供了基于注解的权限控制方案,使用注解去指定访问对应的资源所需的权限,首先开启相关配置
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)
然后就可以使用@PreAuthorize
@RestController
public class HelloController{
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('test')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
实现UserDetailsService接口查询用户和对应的权限信息中需要封装权限信息
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService{
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException{
//查询用户信息
LambdaQueryWapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(User::getUserName,username);
User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWapper);
//如果没有查到用户抛出异常
if(Objects.isNUll(user)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名或者密码错误");
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("test","admin"));
return new LoginUser(user,list);
}
}
返回LoginUser参数限制,添加成员变量和有参构造,实现获取权限的方法
private List<String> permission;
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities;
public LogisUser(User user,List<String> permission){
this.user = user;
this.permission = permission;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GranteAuthority> getAuthorites(){
//把permission中String类型的权限信息封装成SimpleGrantedAuthority对象
List<GrantedAuthority> newList = new ArrayList<>();
for(String permission:permissions){
SimpleGrantedAuthority authority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority();
newList.add(authority);
}
if(authorities!=null){
return authorities;
}
//1.先把permissions转换成流对象2.引用构造器3.然后收集成集合
authorities = permissions.steam().map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new).collect(Collections.toList());
return authorities;
}
需要存入redis,SimpleGrantedAuthority会进行序列化,在方法头添加注释进行忽略,authorities这个成员变量就不会进行序列化
授权使用
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequest{
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
protected void doFillterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain filterChain) throws {
//获取token
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if(!StringUtils.hasText(token)){
// 放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//解析token
try{
Claims claims = Jwt.parseJWT(token);
userId = claims.getSubject();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("token非法");
}
//从redis中获取用户信息
String redisKey = "login"+userId;
LoginUser loginUser = redisCache.getCacheObject(redisKey);
if(Objects.isNUll(loginUser)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户未登录");
}
//存入SecurityContextHolder
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser,null,loginUser.getAuthorities());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication();
// 放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
从数据库查询权限信息
RBAC权限模型:全称为Role-Based Access Control,基于角色的权限控制
定义mapper根据userid查询权限信息
public interface MenuMapper extends BaseMapper<Menu>{
List<String> selectPermsByUserId(Long id);
}
在配置文件中说明mapper的映射的xml文件位置
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations:classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml
自定义失败处理
在认证失败或者授权失败的情况下返回相同结构的json,让前端对响应进行统一的处理
SpringSecurity的异常处理机制
在SpringSecurity中,如果在认证或者授权的过程中出现了异常会被ExceptionTranslationFilter捕获到,在ExceptionTranslationFilter中会判断是认证失败还是授权失败出现的异常
如果是认证过程中出现的异常会被封装成AuthenticationException然后调用AuthenticationEntryPoint对象的方法去进行异常处理
如果是授权过程中出现的异常会被封装成AccessDeniedException然后调用AccessDeniedHandler对象的方法去进行异常处理
如果需要自定义异常处理,需要自定义AuthenticationEntryPoint和AccessDeniedHandler然后配置给SpringSecurity即可
@Component
public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl implements AuthenticationEntryPoint{
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,AuthenticationException authException) throws Exception{
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value,"用户认证失败,请重新登录!");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
//处理异常
WebUtils.renderString(response,json);
}
}
@Component
public class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler{
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,AuthenticationException authException) throws Exception{
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value,"您的权限不足!");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
//处理异常
WebUtils.renderString(response,json);
}
}
在SecurityConfig类中配置
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private AccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler;
//在configure中配置异常处理器
http.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint).accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);
跨域问题解决
浏览器处于安全的考虑,使用XMLHttpRequest对象发起http请求必须遵守同源策略,否则就是跨域的http请求,默认情况下是被禁止的。同源策略要求源相同才能正常进行通信,即协议,域名,端口都完全一致。
前后端分离项目,前端项目和后端项目一般都不是同源的,所以会存在跨域请求的问题。
1、先对SpringBoot配置,运行跨域请求
@Configuration
public class corsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry){
//设置允许跨域的路径
registry.addMapping("/**")
//设置允许跨域请求的域名
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
//是否允许cookie
.allowCredentials(true)
//设置允许的请求方式
.allowMethods("GET","POST","DELETE","PUT")
//设置允许的header属性
.allowedHeaders("*")
//跨域允许时间
.maxAge(3600);
}
}
2、开启SpringSecurity的跨域访问
在SecurityConfig中的configure方法
//允许跨域
http.cors();
权限校验
权限校验方法
hasAuthority
hasAuthority方法实际是调用authentication的getAuthorities方法获取用户的权限列表,然后判断存入的方法参数数据是否在权限列表中
hasAnyAuthority
hasAnyAuthority可以传入多个权限,只要用户有其中任意一个权限都能访问对应资源
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin','test','system:dept:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
hasRole
hasRole要求有对应的角色才可以访问,但是内部会把我们传入的参数拼接上ROLE_后再去比较,所以用户对应的权限也要有ROLE__这个前缀才可以
hasAnyRole
hasAnyRole要求有任意的角色才可以访问
自定义权限校验方法
@Component("ex")
public class SGExceptionRoot{
public boolean hasAuthority(String authority){
//获取当前用户的权限(在filter过滤器中用户信息和权限存入SecurityContextHolder里面)
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();
List<String> permissions = loginUser.getPermission();
//判断用户权限集合是否存在authority
return permissions.contains(authority);
}
}
hasAuthority这个方法名和之前的重名,可以使用@指定特定类,使用@ex相当于获取容器中bean的名字为ex的对象
@PreAuthorize(@ex.hasAuthority('admin')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
基于配置的权限校验
在SecurityConfig配置类中,对接口方法进行权限配置
http.antMatchers("/testCors").hasAuthurity("system:dept:list")
CSRF
CSRF是指跨站请求伪造(Cross-site request forgery),是web常见的攻击之一
SpringSecurity防止CSRF攻击的方式就是通过csrf_token,前端发起请求的时候需要携带这个csrf_token,后端会有过滤器进行校验,如果没有携带或者伪造的就不允许进行访问
CSRF攻击依靠的是cookie所携带的认证信息,但是在前后端分离的项目中项目认证信息是token,token并不是存入cookie中,而是在local storage中,并且需要前端代码去把token设置到请求头中,所以CSRF攻击就不用担心
认证成功处理器
实际上在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter进行登录认证时,如果登录成功会调用AuthenticationSuccessHandler的方法进行认证成功后的处理的。AuthenticationSuccessHandler就是登录成功处理器
SGSuccessHandler
@Component
public class SGSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler{
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Authentication authentication){
System.out.println("认证成功了");
}
}
SecurityConfig
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler;
@Override
protected void configure(HtppSecurity http) throws Exception{
//登录成功后执行登录成功处理器
http.formLogin().successHandler(successHandler);
//Security配置
//对所有请求授权
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
认证失败处理器
实际上在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter进行登录认证时,如果认证失败了会调用AuthenticationFailureHandler的方法进行认证失败后的处理的。AuthenticationFailureHandler就是登录失败处理器
注销成功处理器
实现LogoutSuccessHandler的onLogoutSuccess方法,然后在SecurityConfig配置类中配置注销成功处理器
http.logout().logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler)

